Software Development in Pairs or Groups
The development of new software is not a simple process, depending on the size of the program, a large number of possible junctures, functions and problematic issues must be taken into account. Hence, in recent years other more modern working methods have been developed that allow more efficient programming and generate error-free code.
Pair Programming
What is Pair Programming?
Pair programming specifies that there are always two people working on the code at the same time and as far as possible, they sit together. One is in charge of writing the code and the other of supervising it in real time. At the same time, they are constantly exchanging impressions: they discuss problems, find solutions and develop creative ideas.
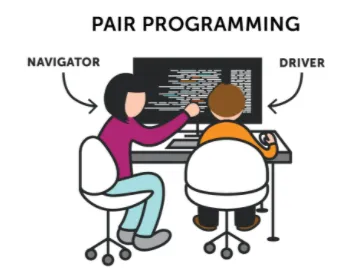
How is it done?
Team size: 2 people.
Roles:
- Driver He is charge of writing the code.
- Navigator: He is charge of supervising that code.
One of the rules of pair programming establishes that these two roles are exchanged regularly, in this way a possible hierarchical gap is avoided.
Types of Pair Programming:
- Backset Navigator: The navigator takes on more of the driver's tactical roles. In backseat navigation, the controller continues to control the keyboard and typing, but the browser dictates syntactic instructions, such as what name to call a variable or what specific method to call. The rear seat navigator style works best with a beginner as a driver and an expert as a navigator, allowing the beginner to learn by doing.
- Ping Pong Pairing: Allows roles to change frequently and forces engineers to pay attention to the coding and testing aspects of development, gaining familiarity with the process.
- Pomodoro: A typical Pomodoro style matching session lasts 25 minutes followed by a 5 minute break. The controller and the browser change positions. After four 25-minute sessions, both programmers take a longer 20-minute break. Force breaks and regular position change help ensure both programmers are always productive, focused, and up-to-date when a session begins.
Benefits
- You can improve overall productivity through the collaboration process.
- Higher quality code as a result of real-time review.
- Better solutions designed through shared collaboration.
- Faster delivery because solutions to challenging problems are found more quickly.
- Greater focus on code and programming task without distractions.
- Unlocking stuck developers.
- Quick feedback.
- Fewer distractions in development teams.
- Shared best practices.
Mob Programming
What is Mob programming?
A group of highly intelligent people with great challenges working as a team to solve challenges creatively, with operational excellence and working focused on delivering constant value.
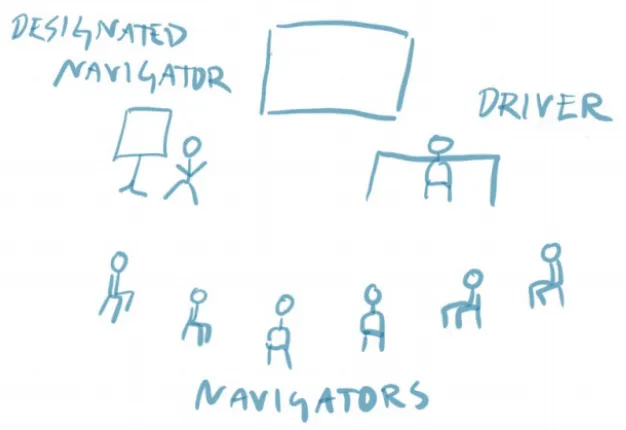
How is it done?
Team size: 3-6 people.
Roles:
- Driver: Receives input from the team and executes the implementation of ideas.
- Navigators: They are the ones that give the driver direction, it is also the voice of the team.
Bias for Action:
- Avoid staying in abstract conversations for a long time.
- Do not discuss a problem for more than 10 minutes (Recommended).
- If there is more than one solution to a problem, experiment with two or 3 (Use paretto).
- Use examples to keep the conversation going.
- The ideas of the browsers are only implemented by the driver.
- The skill level of the driver is key for navigators to further develop the instructions.
- Immediate feedback.
- Learn or contribute.
- Agility in communication.
- Retrospective.
- Empathy and respect.
Artifacts:
- Backlog of specific problems defined by the product owner or the tech lead.
- Alignment in programming katas (New code, bug fixing, test driven development, refactoring).
- Test automation.
- Repo - DevOps.
Types of Mob Programming:
- Expert-Expert: Higher productivity and high-quality results, minimal interruption of approaches and exploration to challenge existing solutions.
- Expert-Novice: Increased opportunity to explore solutions and mentoring opportunities for people new to the team. The novice is more prone to challenging existing solutions and brings disruption, and the expert when teaching can rethink existing paradigms. The risk that experts cannot develop the patience to teach can create conflict and affect the organizational culture.
- Novice-Novice: Normally not recommended for complex solutions, but good for innovation as long as it can be developed with a mentor who can generate a role model.
- With audience: The team is working with an audience of stakeholders or users.
The Value of Mobbing:
- Solutions are delivered faster, with higher quality through increased focus.
- Mitigate tedious tasks, have 360 visibility, and improve automation.
- Leverage training between team members.
- Deliver faster results by reducing work in progress time and eliminating handoff times between teams and mitigating communication problems.
- You can increase the delivery time of a task by the number of people thinking about an individual task, but decrease approx 15% of defects or margin of error, refactoring and rework and support of the task or the deliverable are mitigated.
- Satisfaction increases 96% among programmers.
- Agile training.
- Team building and communication.
- More solution options for several problems at the same time.
Benefits for Other Organizations and Services
- Recruiting.
- Design (Service, UX, Production).
- Tech debt and refactoring.
Information provided by: Julian Alvarado
- Twitter @jascorecr
- Linkedin: alvarado.lj.1
- Telegram: https://t.me/joinchat/JWCCqxZZe7tk7ITpztxTsw
- Youtube: Kata Collective
